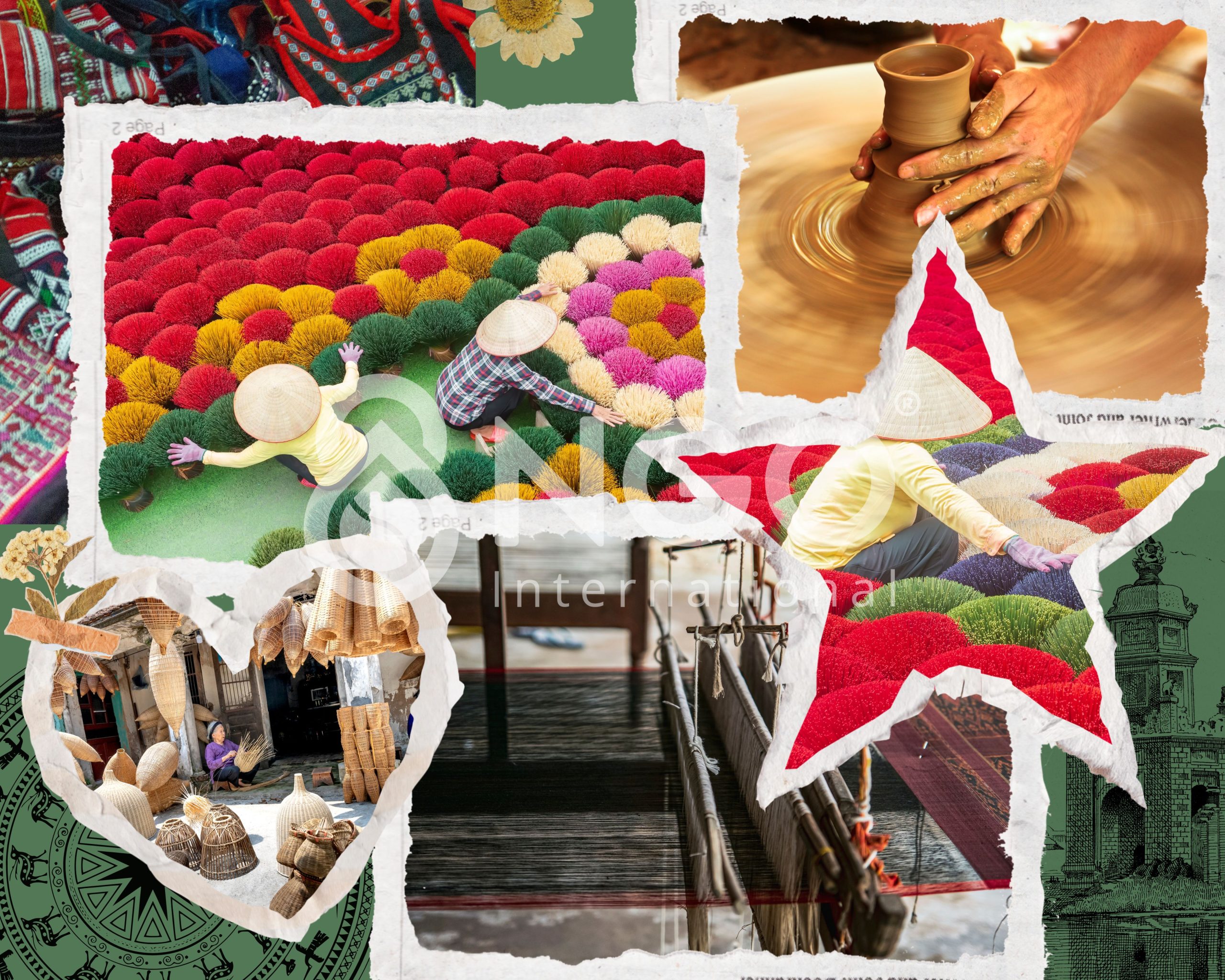
Traditional craft villages play a crucial role in Vietnam’s rural economy, creating jobs for millions of laborers and preserving cultural identity. However, spontaneous development with outdated technology has led to a serious environmental pollution problem, especially water pollution. Wastewater from craft villages often contains high levels of organic matter, toxic chemicals, pathogenic microorganisms, etc., which, if not treated, will have negative impacts on the ecosystem and public health.
According to the 2020 Report on Environmental Protection Work by the Ministry of Agriculture & Rural Development, there are currently 4,575 craft villages nationwide, of which 1,951 are officially recognized, including 1,062 new craft villages and 889 traditional ones. According to the 2020 Report on Environmental Protection Work by the Ministry of Agriculture & Rural Development, only 16.1% of craft villages have a centralized wastewater treatment system that meets environmental protection requirements; the rate of craft villages with industrial solid waste collection points is 20.9%.
1. Composition and properties of craft village wastewater
Wastewater generated from craft villages has a very diverse composition, depending on the type of production. In general, the main pollution parameters commonly encountered include biochemical oxygen demand (BOD), chemical oxygen demand (COD), total suspended solids (TSS), nutrients (nitrogen, phosphorus), oil and grease, microorganisms (Coliform, E. coli), and many other specific pollutants (dyes, heavy metals, chemical solvents, etc.).
|
No. |
Type of Production | Characteristic Pollution Parameters |
|
1 |
Food and beverage processing | BOD₅, COD, TSS, Total N, Total P, Coliform |
|
2 |
Textile dyeing | BOD₅, COD, Color, Total N, chemicals, bleach |
|
3 |
Leather tanning | BOD₅, COD, TSS, metals (Cr⁶⁺), Total N, color, oil and grease |
|
4 |
Paper recycling | pH, BOD₅, COD, TSS, Total N, Total P, color |
|
5 |
Metal recycling | COD, TSS, oil and grease, CN⁻, metal parameters specific to raw materials |
|
6 |
Plastic recycling | BOD₅, COD, TSS, Total N, Total P, color, oil and grease |
|
7 |
Livestock farming, slaughtering | BOD₅, COD, TSS, Total N, Total P, Coliform |
|
8 |
Stone carving and ceramics production | TSS |
|
9 |
Rattan and bamboo weaving | COD |
|
10 |
Metalworking |
Metal parameters specific to raw materials, mineral oil and grease |
Source: National State of the Environment Report for the period 2016 – 2020
Craft village wastewater contains a diverse range of pollutants at high concentrations, far exceeding the environment’s self-purification capacity. Each type of production has its own unique pollution “footprint,” requiring an appropriate treatment process to thoroughly remove specific pollutants.
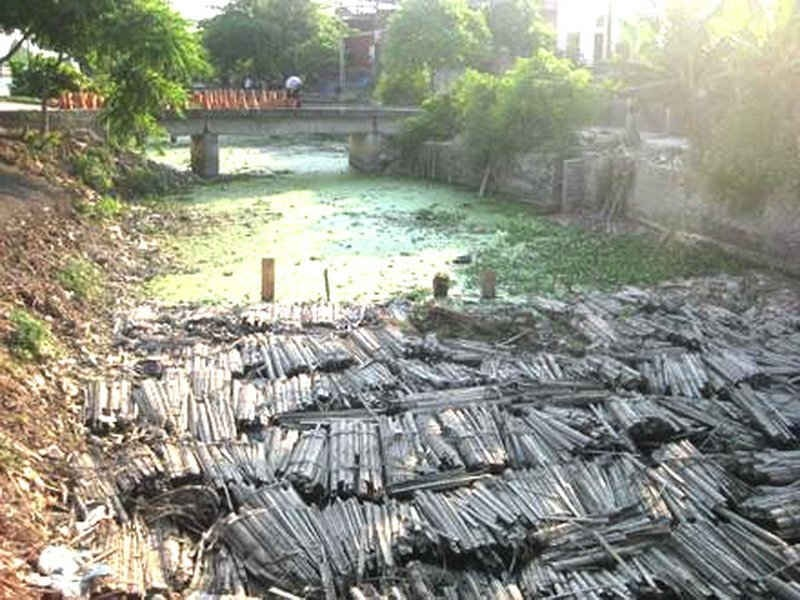

2. Common craft village wastewater treatment processes today
Given the pollution situation described above, the construction of wastewater treatment systems in craft villages is urgent. However, according to the report from the Ministry of Agriculture & Rural Development, only about 16.1% of craft villages have centralized wastewater treatment systems that meet the requirements. The majority of wastewater is still discharged directly into the environment or undergoes rudimentary treatment merely for compliance purposes. Below are the common processes and stages of craft village wastewater treatment currently applied in Vietnam.
- Preliminary treatment (pre-treatment)
- Physico-chemical treatment (coagulation, precipitation, neutralization)
- Biological treatment (aerobic, anaerobic)
- Disinfection and finishing
3. Optimal craft village wastewater treatment solution from NGO International
NGO International has researched and developed a comprehensive and superior craft village wastewater treatment solution with outstanding features:
- Advanced treatment technology: Applying the most modern and advanced technologies available today.
- High treatment efficiency: Reduces up to 95% of BOD, COD, TSS, and thoroughly treats heavy metals and other toxic substances.
- Saves operating costs: Automated system reduces operating and maintenance costs.
- Environmentally friendly: Limits the use of chemicals, reduces emissions, and reuses treated water.
| Evaluation Criteria | Conventional Technology | NGO International Technology |
| BOD Efficiency | 70 – 80% | 95 – 98% |
| COD Efficiency | 60 – 75% | 90 – 97% |
| Energy Consumption | High | Low |
| Automation Level | Medium | High |
| Operating Cost | High | Low |
The solution from NGO International not only meets strict environmental regulations but also ensures sustainability, helping craft villages develop their economy in tandem with protecting their living environment.
Businesses interested in Craft Village Wastewater Treatment Solutions please contact NGO via Phone 024.7300.0890 or email office@8ngo.com for a direct consultation.

***Please carefully read the Terms of Use – Copyright before copying or quoting the content and images of this website.
This website is copyrighted by NGO International Co., Ltd (NGO International). Any use or copying of part or all of the content in any form is strictly prohibited, except with explicit written permission from Us.
 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt





