Vietnam’s garment industry is one of the key economic industries that attracts many laborers and brings a lot of foreign currency to the country. However, in the value chain of the industry, there are many production stages such as dyeing, printing, completing, industrial washing, discharging large amounts of wastewater, which has great impact to the environment.

It is estimated that the amount of wastewater discharged from the textile dyeing processes is very large; from 120 to 300m3/ton of fabric, the weaving and dyeing stage requires from 12 to 65 liters of water for 1 meter of fabric and discharges from 10 to 40 liters of water. Textile wastewater is very diverse and complex. According to calculations from the types of chemicals used such as: dyes, surfactants, electrolytes, lozenges, media, starch, enamel, oxidants …There have been hundreds of typical chemicals such as solutes and heavy metals.
1. Composition and characteristics of textile dyeing wastewater
Wastewater from textile industry includes main pollutants: High temperature, impurities separated from textiles such as grease, nitrogen-containing compounds, pectin, dirt sticking to fibers; chemicals used in technological processes such as starch starch, H2SO4, CH3COOH, NaOH, NaOCl, H2O2, Na2CO3, … dyes, auxiliaries, soak, colorant, detergent. The amount of chemicals used depends on the type of fabric, color and mainly goes to the wastewater of the manufacturing stage.
1.1 Pollutants and wastewater characteristics of textile and dye industry
|
(Source: Wastewater treatment technology using biological methods – Assoc. Prof. PhD. Luong Duc Pham)
1.2 Wastewater characteristics of some dyeing factories in Vietnam
|
Parameter |
Unit |
Woven cotton products |
Knitwear products |
Woolen textiles |
Fiber |
|
Wastewater |
m3/t. of textile |
394 |
264 |
114 |
236 |
|
pH |
– |
8 – 11 |
9 – 10 |
9 |
9 – 11 |
|
TSS |
mg/l |
400 – 1000 |
950 – 1380 |
420 |
800 – 1300 |
|
BOD5 |
mg/l |
70 – 135 |
90 – 220 |
120 – 130 |
90 – 130 |
|
COD |
mg/l |
150 – 380 |
230 – 500 |
400 – 450 |
210 – 230 |
|
Color |
Pt – Co |
250 – 600 |
250 – 500 |
260 – 300 |
– |
(Source: Faculty of Environment – Hanoi University of Science, 2004)
1.3 The composition of dyeing wastewater is presented in the following table:
|
Indicator |
Unit |
Result |
||
|
Activated substance wastewater |
Sulfur wastewater |
Bleaching wastewater |
||
|
pH |
– |
11-Oct |
>11 |
>12 |
|
COD |
mg/l |
450 – 1.500 |
10.000 – 40.000 |
9.000 – 30.000 |
|
BOD5 |
mg/l |
200 – 800 |
2.000 – 10.000 |
4.000 – 17.000 |
|
Total N |
mg/l |
5 – 15 |
100 – 1.000 |
200 – 1.000 |
|
Total P |
mg/l |
0.7 – 3 |
7 – 30 |
10 – 30 |
|
SS |
mg/l |
– |
– |
– |
|
Color |
Pt-Co |
7.000 – 50.000 |
10.000 – 50.000 |
500 – 2.000 |
|
Turbidity |
FAU |
140 – 1.500 |
8.000 – 200.000 |
1.000 – 5.000 |
(Source: Faculty of Environment – Ho Chi Minh City University of Technology)
Basically, textile-dyeing wastewater often has high temperature, high level of color, pH> 9, high BOD and COD. On the other hand, wastewater from textile industry contains some chemicals with heavy metals, toxic components that not only destroys aquatic organisms but also has negative and direct impact on human life.
Current technology of textile wastewater treatment
2. Wastewater treatment technology of textile and dyeing industry is currently applying common technologies:
- Combination of chemical-physical method (coagulation / flocculation) and filtration;
- Combination of chemical-physical method and aerobic biological treatment or vice versa;
- Combination of chemical-physical method, aerobic biological and chemical-physical treatment;
- Combination of chemical-physical method, biological treatment and filtration (sand filter or activated carbon)
Diagram of the current technological process of textile dyeing wastewater treatment:

In general, the traditional technologies currently applied to the textile wastewater treatment still have many difficulties for businesses, for example:
- Using chemicals mainly can eliminates dispersed colors only, more complex color components such as reactivation and reconstitution are often impossible to be removed.
- When using many chemicals, operating costs will be very high, it is especially difficult to quantify chemicals for flocculation steps, or Fenton due to production by order, color composition and pollution concentration of wastewater often fluctuates according to orders.
- Microbiological systems are often large, requiring a lot of space
NGO with breakthrough solution to color treatment
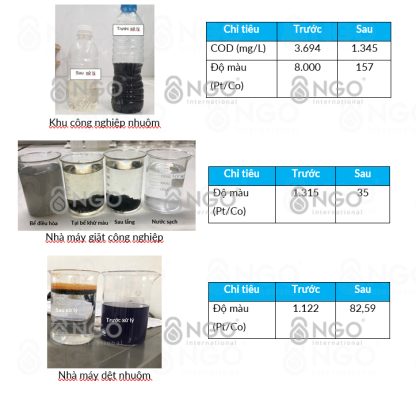
• Eliminates above 95% of all colors, including activated color, no use of flocculating or decolorizing chemicals, less produced sludge.
• Color treatment efficiency is independent of the microbiology and weather fluctuations • Results are visible on the first day of operation, without waiting
NGO với giải pháp ĐỘT PHÁ trong xử lý màu
- Eliminates above 95% of all colors, including activated color, no use of flocculating or decolorizing chemicals, less produced sludge.
- Color treatment efficiency is independent of the microbiology and weather fluctuations
- Results are visible on the first day of operation, without waiting
3. Practical case studies in Vietnam
Tại Saitex Đồng Nai, nhà máy đã áp dụng giải pháp ZERO DISCHARGE (0 xả thải) cho hệ thống xử lý nước thải Demin với công suất 1000 m3/ngày đêm, sử dụng các công nghệ tiên tiến gồm: VI SINH – ĐIỆN PHÂN KEO TỤ – LỌC UF & RO
- Tái tuần hoàn nước 98%
- Thời gian hoàn vốn đầu tư cho toàn bộ hệ thống ~ 2 năm
- Không cần quan trắc chất lượng nước định kỳ với cơ quan chức năng do không xả thải
* Color treatment process is extremely simple: Textile wastewater is firstly collected to the flow equalization basin with aeration, and then pumped onto the Decoloring Device by electrolytic oxidation; at this step, metal ions and electrons are generated, creating redox reactions to break down the emulsion, destroy colloids and suspended solids. Fe ++ or Al ++ ions are released from the electrode, creating stable flocculants to remove most of the color in wastewater by flotation or gravity deposition or mechanical filtration, leaving the clear water be discharged or pumped into the next treatment facility. In particular, the contaminated components including heavy metals, grease and most of the COD are also removed at the same time of color treatment.
3. Practical case studies in Vietnam
https://style-republik.com/saitex-nha-may-san-xuat-jeans-tac-dong-moi-truong/
Mores: Wastewater treatment of textile and dyeing industry video: hhttps://www.youtube.com/watch
More:
https://shopngoenvironment.com/product-category/san-pham-cong-nghiep/thiet-bi-loc/
https://shopngoenvironment.com/product/mang-ro-xu-ly-nuoc-thai/
https://shopngoenvironment.com/product/thiet-bi-mang-loc-e-mbr/
https://shopngoenvironment.com/product/mang-loc-mbr-x/
https://shopngoenvironment.com/product/thiet-bi-keo-tu-dien-phan-ec/

***Vui lòng đọc kỹ yêu cầu về Điều khoản sử dụng – Bản quyền trước khi sao chép hoặc trích dẫn nội dung và hình ảnh của website.
Trang web này thuộc bản quyền của Công ty TNHH Quốc tế NGO (NGO International). Bất kỳ hình thức sử dụng hoặc sao chép một phần hoặc toàn bộ nội dung dưới mọi hình thức đều bị nghiêm cấm, trừ trường hợp được sự cho phép rõ ràng bằng văn bản từ Chúng tôi.
 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt





