According to data from the Ministry of Planning and Investment as of the end of January 2025, the country currently has about 433 operational Industrial Parks out of a total of 575 in the national development plan for Industrial Parks in Vietnam, which was approved by the Prime Minister to extend to 2030. The number of Industrial Clusters is projected to reach 1,849.
Vietnam is emerging as a new industrial manufacturing hub in the Asian region and is receiving an ever-increasing wave of FDI investment. Consequently, the number of investment projects in the infrastructure of industrial parks and industrial clusters is very dynamic.
For infrastructure developers, the pressure of increasingly strict regulatory compliance, the investment and operational costs of wastewater treatment systems, along with the demand for “Green Value” and “Sustainable Development” to attract secondary investors, are becoming a complex challenge. Is there a solution that both ensures treatment efficiency and legal compliance, while also optimizing costs and enhancing the “green” image for the Industrial Park?
THE DEVELOPER’S CHALLENGE

Regulatory Compliance Pressure

High Initial Investment Costs

Demand for ‘Green Value’ & Sustainability

Choosing Appropriate Technology
I. Common Wastewater Treatment Technologies for Industrial Parks and Clusters in Vietnam
In Vietnam, the majority of centralized wastewater treatment systems for industrial parks and clusters use the following three groups of technologies:
|
CRITERIA |
TECHNOLOGY 1 |
TECHNOLOGY 2 |
TECHNOLOGY 3 |
|
Physicochemical + A-O Biological Treatment |
Physicochemical + SBR or ASRB |
Physicochemical + Biological + MBR |
|
|
Main Steps in the Process Flow |
1. Collection Tank 2. Equalization Tank 3. Coagulation and Flocculation Tank (PAC Polymer) 4. Physicochemical Clarifier 5. Anoxic Tank 6. Aerobic Tank 7. Biological Clarifier 8. Disinfection & Discharge Chamber 9. Sludge Tank |
1. Collection Tank 2. Equalization Tank 3. Coagulation and Flocculation Tank (PAC Polymer) 4. Physicochemical Clarifier 5. SBR (Sequencing Batch Reactor) Tank 6. Disinfection & Discharge Chamber 7. Sludge Tank |
1. Collection Tank 2. Equalization Tank 3. Coagulation and Flocculation Tank (PAC & Polymer) 4. Physicochemical Clarifier 5. Anoxic Tank 6. Aerobic Tank 7. MBR (Membrane Bioreactor) Tank 8. Disinfection & Discharge Chamber 9. Sludge Tank |
|
Advantages |
– Simple design – Effective Total Nitrogen (TN) removal – Easy to adjust during operation |
– Smaller treatment tank volume than Technology 1 – Saves construction area – Operation of phases in the batch reactor is typically fixed, with little room for adjustment when needed during operation |
– Effluent quality is generally stable and better than Technology 1 & 2 thanks to the MBR membrane filtration step – Saves construction area |
|
Disadvantages |
– A-O biological tanks typically require a large area |
– When influent TN or Ammonia levels fluctuate highly, it is often difficult to meet discharge standards. |
– Investment cost is typically higher than Technology 1 & 2 |
II. NGO Partners with Infrastructure Developers
NGO’s goal is not to SELL OFF-THE-SHELF SOLUTIONS; instead, we aim to PARTNER with developers, acting as the BEST COST-EFFECTIVE CONSULTING PARTNER throughout the journey of building, developing, and maintaining Industrial Parks and Clusters.
WE PROVIDE
- Consulting on pollution treatment plans tailored to each development phase of the industrial park, industrial cluster while ensuring compliance with legal requirements
- Technology suitable for both discharge purposes and for water reclamation or landscaping.
Reduce up to
50%
Treatment tank area
Reduce up to
35%
Construction cost
OUR COMMITMENT
- Operational management support to ensure water quality meets design specifications
- Support for the developer regarding legal compliance
- Consulting on circular economy initiatives, adding value in the IP, IC
NGO continuously improves and innovates, optimizing its design solutions through experience accumulated from each project, as well as technology transfer from reputable global partners.
III. Featured Client
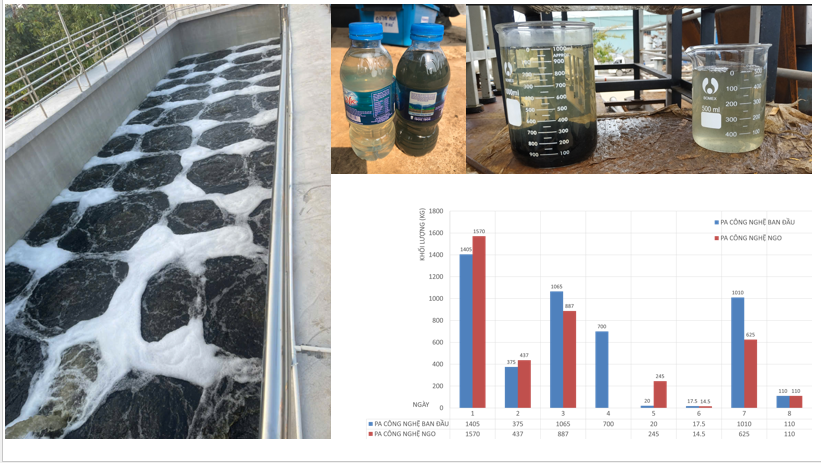
- Client: A Textile & Dyeing Industrial Cluster in Northern Vietnam
- Challenge: The existing wastewater treatment system was overloaded in terms of capacity and influent pollution load, frequently failing to meet QCVN 40:2011/BTNMT Grade A standards. Operational costs were high due to extensive chemical usage, and there was no available space to expand the treatment tanks.
- NGO International’s Solution:
- Surveyed & re-evaluated the wastewater characteristics from factories discharging to the IC
- Stabilized flow rate and pollutant concentrations to reduce daily fluctuations
- Readjusted the technological principles between the existing tanks
- Result:
- Reduced daily water quality fluctuations; the treatment efficiency of each technology unit improved by 20% – 56%, leading to stable operation with fewer incidents.
- Operational chemical costs reduced by 30% (reduction in decolorizing agents, pH adjustment chemicals, etc.)

“Working with NGO gives us great confidence because the daily operational analysis data is always clear. After NGO’s upgrade, we have significantly cut chemical operating costs and reduced the number of operational staff at the plant.” – Mr. Do Quoc Cuong, Director of the IC Management Board.
Wastewater Treatment Video for Industrial Parks and Clusters
IV. Frequently Asked Questions
The cost depends on many factors: capacity scale, wastewater composition and pollutant concentration, selected technology, required effluent quality, and site conditions. NGO International will conduct a survey and advise on the most cost-effective solution for each specific project.
The construction time also varies depending on the scale and technological complexity. Small to medium-sized projects may take 3-6 months, while larger projects can take from 6-12 months or more. NGO is committed to a swift timeline while ensuring quality.
The main national technical regulation is QCVN 40:2011/BTNMT for industrial wastewater. Additionally, depending on the specific industries within the IP (e.g., textiles have QCVN 13-MT:2015/BTNMT, paper has QCVN 12-MT:2015/BTNMT), there may be separate industry-specific standards.
Absolutely. With advanced technologies, the quality of treated water can meet reuse standards for many purposes such as irrigation, cooling systems, industrial cleaning, road washing, and even some production processes with less stringent water quality requirements. This helps save on fresh water costs and protect resources.
Beyond legal compliance, a modern system helps to: reduce long-term operational costs, enhance the IP’s reputation and “green” image, attract high-quality investors, minimize the risk of environmental incidents, create opportunities for water reuse, and contribute to overall sustainable development.
Read more at:
Businesses interested in Wastewater Treatment Solutions for Industrial Parks and Clusters, please contact NGO via phone at 024.7300.0890 or email office@8ngo.com for a direct consultation.

***Please carefully read the Terms of Use – Copyright notice before copying or citing the content and images of this website.
This website is copyrighted by NGO International Co., Ltd. Any use or copying of all or part of the content in any form is strictly prohibited, except with explicit written permission from Us.
 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt