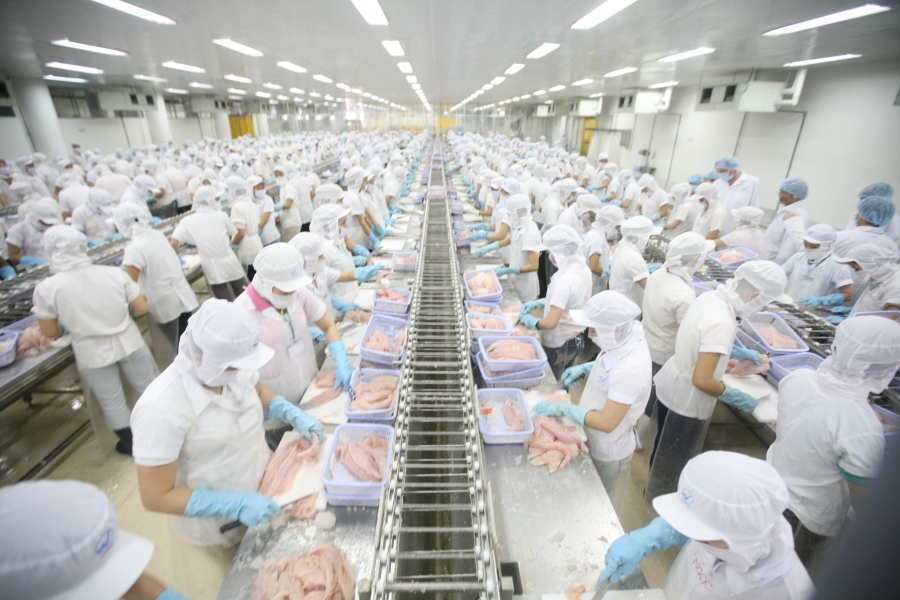
NGO News – Vietnam is one of the leading seafood exporters in the world. Major products in seafood exporting sector are pangasius, pangasius bocourti, shrimps and molluce such as squid, octopus, clams, cockles … Rapid growth speed of the industry causes the rise of seafood processing wastewater, thereby highly affects the environment.

1. Impact of seafood wastewater on environment
Some of the typical impacts of the seafood processing industry on the environment are as follows:
- Air pollution: odors generating from the storage site of waste in the prodcution process; emission from the backup generators. In air pollution sources, odor is a major problem for seafood processing plants.
- Solid waste mainly arises from food processing, consisting of fish shells and heads…
- Wastewater in seafood processing accounts for 85-90% of total wastewater, mainly from the following processes: washing, processing, finishing, factory & eqipment cleaning, and domestic waste water.
2. Sources of production water/waste
The amount of waste and the concentration of substances discharging from seafood processing depends mainly on: (i) the components of the raw material, (ii) the used additives, (iii) water source; (iv) stages in the production process such as raw materials processing, slaughtering, boiling, impregnating, steaming, factory & tools cleaning.
- Wastewater from raw material processing is wastewater from thawing, washing of raw materials, barrels, and packing materials. Depending on the types of material (shrimps, fish, cuttlefish, octopus, crabs, and oysters), the size of the material, the storage time, the level of sanitary water use, Wastewater has different concentration of pollution and fluctuations: BOD varies between 1000 – 10,000 mg/L, oxidation (CODMn) is about 30% of BOD [9]. Wastewater is highly contaminated with insoluble residue, protein, fish oil and fat in disperse form and blood.
- Wastewater from boiling, steaming, marinating is a process that follows the preliminary process. Boiled water contains protein, fat, mineral salts with high concentration. Wastewater is usually recovered to produce fish meal (dried with fish meal).
- Wastewater from the slaughtering stage: finning, filleting, squid… Waste water from shrimp, squid and octopus processing has higher level of pollution than frozen fish processing.
3. Flow and characteristic of seafood processing wastewater
In the seafood processing process, differences in raw materials and end products involve the differences in the production process, resulting in different water consumption. Also refer to the amount of water used in processing some types of seafood:
- Catfish: 5-7 m3 / ton of product
- Frozen shrimp: 4-6 m3 / ton of product
- Surimi (crab product): 20-25 m3 / ton of product
- Combined frozen seafood: 4-6 m3 / ton of product
Characteristics of aquatic processing wastewater: color, odor, insoluble solids, suspended solids, disease germs, dissolved organic substances, nutrients…
- COD fluctuates between 500 – 3000 mg / l, COD is about 300 – 2000 mg / l, Nitrogen is quite high at 50-200 mg / l. Wastewater has high levels of organic matter and nutrients, including carbohydrate, protein, and lipid – these are biodegradable substances. In addition, waste water also contains oil, phosphate, nitrate, fat, detergents, etc.
- Suspended solids (SS) fluctuates from 200 – 1000 mg / l, due to the presence of debris and debris that are easily deposited. In addition, sludge and sand swept with water when washing, preliminary processing of raw materials or equipment & factory cleaning.
- Odorl, H2S, NH3 produced by decomposition of aquatic debris in wastewater or incomplete anaerobic decomposition of protid compounds and other acids. Cl2 odor generates during sterilization.
- Color: Color of wastewater is due to domestic wastes and blood of aquatic animals during processing
- Pathogenic germs.
Current treatment methods mainly include 3 levels of treatment: Level 1: Pretreatment includes raw waste separation, grease separator, TSS removal; Level 2: microbiological treatment; Level 3: Sedimentation, filtration, sterilization with a common retention time of 30-40 hrt towards A standard.
With the development of environmental technology, more and more effective solutions and technologies come out, but not all solutions are suitable and easy to apply for enterprises due to high investment costs. In order to optimize the cost of investment and operation, the process should be simplified based on the knowledge of the designer as well as the integration of the solution. For more information of the new solutions, please leave your questions here or contact us at (024) 3 5668225.
***Vui lòng đọc kỹ yêu cầu về Điều khoản sử dụng – Bản quyền trước khi sao chép hoặc trích dẫn nội dung và hình ảnh của website.
Trang web này thuộc bản quyền của Công ty TNHH Quốc tế NGO (NGO International). Bất kỳ hình thức sử dụng hoặc sao chép một phần hoặc toàn bộ nội dung dưới mọi hình thức đều bị nghiêm cấm, trừ trường hợp được sự cho phép rõ ràng bằng văn bản từ Chúng tôi.
Nguồn: NGO
 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt