
In recent years, Vietnam’s beverage industry has contributed more than 10% to the national GDP, maintaining an impressive growth rate. The average annual growth of this segment is expected to reach 6.28% from 2023 to 2028.
As the demand for beverages increases, the supply chain for aluminum packaging (aluminum cans) has also expanded. Aluminum cans, in particular, have the advantage of being more recyclable than other packaging materials, aligning with businesses’ efforts toward sustainable packaging.
1. Aluminum Can Production Process
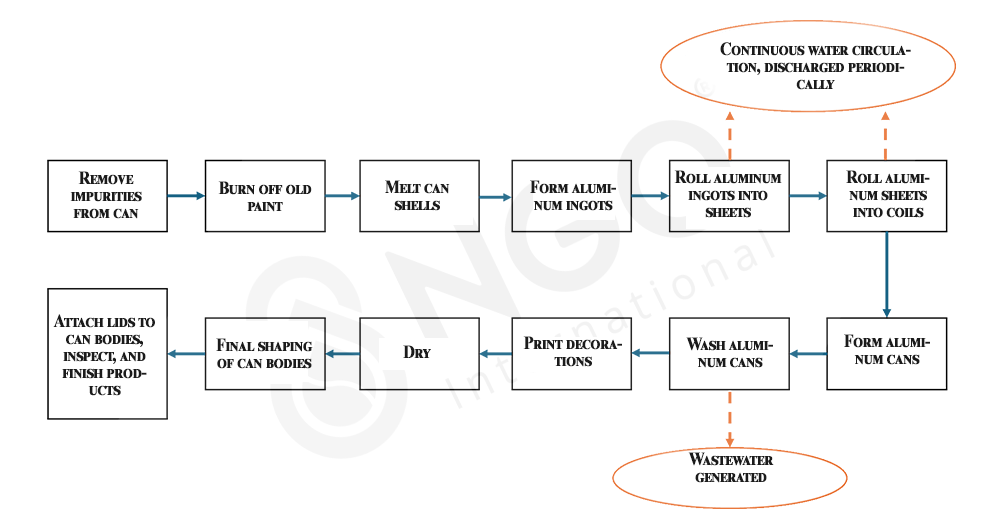
2. Challenges in Treating Aluminum Can Production Wastewater
a. Characteristics of Wastewater
The composition and characteristics of aluminum can production wastewater primarily include heavy metals, mineral oils, and organic compounds.
-
Heavy metals such as aluminum, chromium, nickel, and cadmium may appear in wastewater from plating, anodizing, and protective coating processes.
-
High COD and BOD levels: Organic compounds from paints, inks, and surface treatment chemicals contribute to high chemical oxygen demand (COD) and biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) levels in aluminum can production wastewater.
-
High suspended solids (TSS): Suspended solids often include aluminum dust, aluminum scraps, and residual contaminants from cutting, stamping, and machining processes.
| Parameter | Unit | Concentration Range | Source |
| Heavy Metals | |||
| Aluminum (Al³⁺) | mg/l | 150-300 | Cleaning, anodizing, protective plating |
| Crom (Cr⁶⁺, Cr³⁺) | mg/l | 0,1 – 5 | Anodizing, corrosion resistance |
| Niken (Ni²⁺) | mg/l | 0,1 – 3 | Protective plating, aluminum alloys |
| Zinc (Zn²⁺) | mg/l | 0,2 – 10 | Coating, corrosion resistance |
| pH | – | 3 – 12 | Acidic or alkaline cleaning |
| Solids | |||
| Total Suspended Solids (TSS) | mg/l | 200 – 500 | Sludge, metal residues |
| Organic Compounds & Oils | |||
| Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) | mg/l | 200 – 1000 | Cleaning chemicals, oil emulsions |
| Mineral Oils | mg/l | 10 – 400 | Lubricants, surface protectants |
| Other Compounds | |||
| Amoni (NH₄⁺-N) | mg/l | 5 – 50 | Additive chemicals |
| Sunfat (SO₄²⁻) | mg/l | 200 – 2000 | Sulfuric acid use in anodizing |
📌 Note: The concentration ranges in the table are for reference only. Actual values may vary depending on production technology and pollution control measures at each factory.
3. Wastewater Treatment Solutions by NGO International
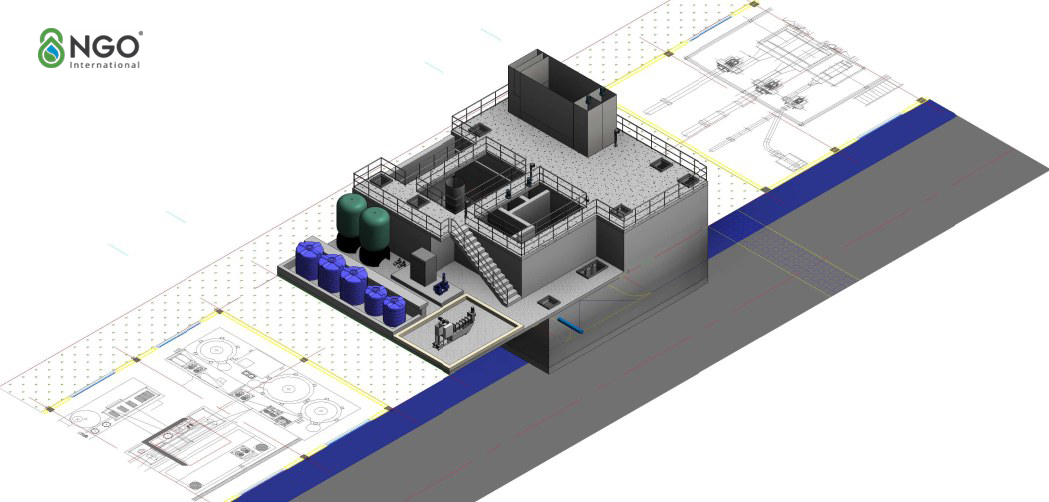
a. Compact Treatment System with Small Footprint
NGO International designs systems that effectively separate and pre-treat highly polluted wastewater streams, reducing the overall pollution load. This approach optimizes reaction tank volumes and minimizes construction space.
b. Cost-Optimized Investment
With extensive expertise in wastewater characteristics and contaminants, NGO International optimizes designs using 100% locally manufactured equipment in Vietnam, reducing investment costs.
c. Wastewater Recycling & Reuse
Currently, treated wastewater meets QCVN 40:2025/BTNMT standards and is discharged into the environment. However, as environmental concerns grow and clean water becomes scarcer, simply meeting discharge standards is no longer the most economical or effective solution for modern industries. In line with sustainable development trends, wastewater reuse is becoming a strategic approach.
Instead of wasting valuable resources, treated wastewater can be recycled for production, aiming toward a zero-discharge factory model.
Businesses interested in wastewater treatment solutions for aluminum can production can contact NGO International at +84 24 7300 0890 or email office@8ngo.com for direct consultation.
See more at:
https://shopngoenvironment.com/en/product-category/industrial-products/flotation-equipment/

***Please carefully read the Terms of Use – Copyright Policy before copying or quoting any content and images from this website.
This website is copyrighted by NGO International Co., Ltd. Any use or reproduction of part or all of the content in any form is strictly prohibited, except with explicit written permission from us.
 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt





