DOMESTIC WASTEWATER TREATMENT TECHNOLOGY
1. Characteristics of domestic wastewater
What is domestic wastewater?
Domestic wastewater is generated from daily human acitivities such as: bathing, eating & drinking, cleaning…Except for individual household which has not been applied any regulations on domestic wastewater treatment, all buildings, commercial centers, resorts, factories, and restaurants… have to treat domestic wastewater in accordance with QCVN 14:2008/BTNMT – National technical regulation on domestic wastewater.
Compositions of domestic wastewater:
According to polluted characteristics, domestic wastewater is divided into two types: blackwater (from toilet and septic tank), greywater (from bathing, eating & drinking actitivies). Blackwater has high concentration of BOD, ammonium, pathogenic microorganisms which are the main polluted sources in domestic wastewater.
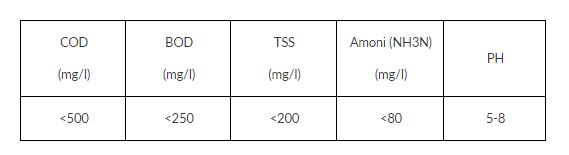
Pollution parameters of normal domestic effluent (including all sources from bathing, eating & drinking, cleaning) are as follows:
 However, at many factories and commercial centers when greywater is rare (due to not have bathing activities), polluted concentration is often higher, especially the concentration of ammonia from blackwater. Ammonium concentration is generally higher than 100mg/l, upto 150mg/l. At present, most of domestic wastewater treatment projects in Vietnam still face difficulties in thoroughly treating ammonia.
However, at many factories and commercial centers when greywater is rare (due to not have bathing activities), polluted concentration is often higher, especially the concentration of ammonia from blackwater. Ammonium concentration is generally higher than 100mg/l, upto 150mg/l. At present, most of domestic wastewater treatment projects in Vietnam still face difficulties in thoroughly treating ammonia.
In many projects, the unbalanced proportion of COD/BOD and BOD/NH3N in wastewater causes difficulty for microorganisms development to treat pollutants. Especially in Vietnam, most of projects have already built their own traditional septic tank and microbial reactions at septic tank decrease COD concentration which can create obstacle for maintaining high biomass concentration in the next treatment tanks.
2. QCVN 14:2008/BTNMT – National technical regulation on domestic wastewater
Depending on after-treatment wastewater receiving sources are used for the purpose of domestic water supply or not, investors shall select A standard or B standard outlet parameters as per QCVN 14:2008/BTNMT.
3. Popular wastewater treatment technologies:
Due to the fact that BOD/COD level of domestic waste water is normally 0.2 time higher, therefore it can be efficiently treated by microorganisms. This is also considered as the most popular and cheapest treatment method at present. Physico-chemical treatment methods may be added depending on the solution of each supplier and the used technology.
The wastewater treatment method by microorganism is usually applied based on conventional technology or membrane technology, in which traditional solution providers in Vietnam still occupy great number because of the simplicity of solution, depending mainly on microbiology and construction area. However, the quality of after-treatment water is often unstable if the footprint area is small. In addition, the construction investment cost are high.
There are some popular technologies applied in domestic wastewater treatment:
Conventional activated sludge technology (CAS)
- Activated sludge is the method by which microorganisms in the waste water adhere to the suspended substances in which they reside, reproduce, and grow. These microorganisms use organic matter in water as food and decompose organic matter to gradually create sludge flocs which are called activated sludge
- Water quality after treatment depends on the sedimentation ability of activiated sludge and size of the reactor tanks.
Anaerobic-Anoxic-Aerobic (AAO)
- AAO wastewater treatment technology is a sequential biological treatment system using a variety of microorganisms, including anaerobic microorganisms, anoxic and aerobic microorganisms. AAO technology uses microorganisms that adhere to suspended substances to reside as conventional activated sludge technology (CAS) but is more comprehensive.
Moving bed biofilm membrane (MBBR)
- The nature of MBBR is CAS/AAO/AO process, with additional moving beds. Moving beds help to increase the surface area for the adhesion of micro-organisms, hence the concentration of MLSS can increase significantly. The most concentration of MLSS, the less footprint requires for effluent treatment system.
MBR Solution
- MBR is advanced technology using biological method combined with biomass separation technique using MF/UF membranes with a pore size ranging from 0,1 – 0,4 µm. Biological treatment process can combine anaerobic-anoxic-aerobic (AAO/AO) steps depending on the treatment requirement or processing of organic matter thoroughly both nutrients (N,P).
4. Components of a typical domestic wastewater treatment plant/system
A typical domestic wastewater treatment system/plant is usually constructed with the following main components:
- Collection system: Collect wastewater from different discharge sources to one collection tank
- Pretreatment system: Use coarse screening or fat removal.
- Microbiological treatment system: Include anaerobic, anoxic or aerobic treatment tank.
- Post-treatment system: Include sedimentation tank, sludge collection tank, sterilization tank.
- Control system and operation house.
- Sludge pressing equipment: Used for projects with large discharge capacity.
A system/plant that includes all of the above components does not mean that it is an effective wastewater treatment system. The design specifications, the proper installation of the equipment, the standard operation of every technology will determine the treatment quality of the system, depending on the knowledge and experience of each solution provider. In addition, the operation cost of entire system to produce 1m3 of clean water from wastewater is also an important criterion for evaluating the system quality.